Introduction
The human heart, a tireless pump that beats approximately 100,000 times a day, is a marvel of biological engineering. It's a muscular organ about the size of a fist, located slightly to the left of the chest. Despite its relatively small size, the heart plays a vital role in sustaining life by circulating blood throughout the body.
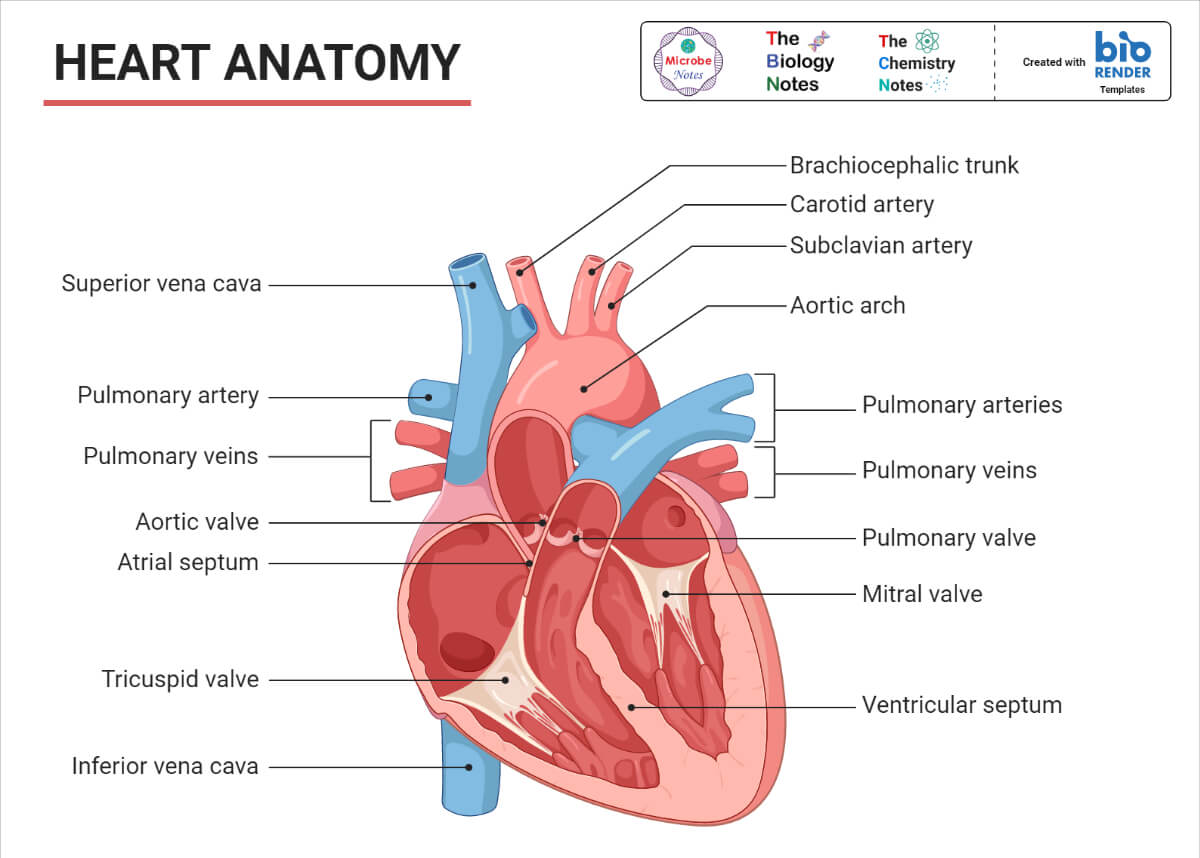
Anatomy of the Heart
The heart is composed of four chambers: the right atrium, the right ventricle, the left atrium, and the left ventricle.
- Right Atrium: This chamber receives deoxygenated blood from the body through the superior and inferior vena cavae.
- Right Ventricle: This chamber pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery.
- Left Atrium: This chamber receives oxygenated blood from the lungs through the pulmonary veins.
- Left Ventricle: This chamber pumps oxygenated blood to the body through the aorta.
The heart is surrounded by a protective sac called the pericardium. The pericardium helps to anchor the heart in place and prevents excessive movement.
The Cardiac Cycle
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events that occurs during one heartbeat. It consists of two phases: diastole and systole.
- Diastole: This is the relaxation phase of the cardiac cycle. During diastole, the atria and ventricles fill with blood.
- Systole: This is the contraction phase of the cardiac cycle. During systole, the ventricles contract and pump blood out of the heart.
The cardiac cycle is regulated by the electrical activity of the heart. The electrical activity is generated by a specialized group of cells called the sinoatrial (SA) node, which is located in the right atrium. The SA node acts as the heart's natural pacemaker, generating electrical impulses that cause the heart to contract.
Blood Circulation
The heart plays a crucial role in blood circulation. Blood is pumped throughout the body by the heart, delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells and removing waste products.
- Pulmonary Circulation: This is the circulation of blood between the heart and the lungs. Deoxygenated blood is pumped from the right ventricle to the lungs through the pulmonary artery. In the lungs, the blood picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. Oxygenated blood
is then returned to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins. - Systemic Circulation: This is the circulation of blood between the heart and the body. Oxygenated blood is pumped from the left ventricle to the body through the aorta. In the body, the blood delivers oxygen and nutrients to cells and removes waste products. Deoxygenated blood is then returned to the right atrium through the superior and inferior vena cavae.
The Heart's Blood Supply
The heart itself requires a constant supply of blood to function properly. The heart's blood supply is provided by the coronary arteries, which branch off from the aorta. The coronary arteries deliver oxygenated blood to the heart muscle.
Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
Heart rate is the number of times the heart beats in one minute. A normal heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats per minute. Blood pressure is the force of blood against the walls of the arteries. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). A normal blood pressure is considered to be less than 120/80 mm Hg.
Heart Health
Heart health is important for overall health. There are several lifestyle factors that can help to promote heart health, including:
- Healthy diet: A healthy diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats.
- Regular exercise: Regular exercise can help to improve heart health by strengthening the heart muscle and improving blood circulation.
- Weight management: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of heart disease.
- Stress management: Stress can contribute to heart problems.
- No smoking: Smoking damages the blood vessels and increases the risk of heart disease.
- Limited alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the heart.
Heart Disease
Heart disease is a leading cause of death worldwide. There are several types of heart disease, including:
- Coronary artery disease: This is the most common type of heart disease. It is caused by a buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries, which can lead to a heart attack.
- Heart failure: This occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs.
- Arrhythmias: These are abnormal heart rhythms.
- Congenital heart defects: These are heart defects that are present at birth.
Heart Surgery
Heart surgery is a common treatment for heart disease. There are several types of heart surgery, including:
- Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG): This surgery is used to treat coronary artery disease. During CABG surgery, a healthy blood vessel is grafted onto the heart to bypass a blocked coronary artery.
- Angioplasty: This procedure is used to treat coronary artery disease. During angioplasty, a balloon is inserted into the blocked coronary artery and inflated to open it up.
- Heart valve replacement: This surgery is used to replace a damaged heart valve.
- Heart transplant: This surgery is used to treat severe heart failure. During a heart transplant, a diseased heart is replaced with a healthy heart from a donor.
Conclusion
The human heart is a complex and vital organ that is essential for life. By understanding the anatomy, physiology, and health of the heart, we can take steps to protect our heart health and prevent heart disease.


0 Comments